One-time customer invoicing or one-time consumer invoicing typically refers to invoicing a consumer customer that is done only once.
The workshops organised by the Real-Time Economy project determined how it is possible to implement one-time invoicing of consumer customers in Finland. When the workshops started, the solutions on the market did not allow for sending an e-invoice directly to a consumer, because the consumer must first make an invoice acceptance agreement with the invoicer in their online bank. A service description and instructions on the digitalisation of one-time invoicing aimed at consumers were created in the workshops.
Overview of one-time invoicing
The change enabling one-time invoicing is made so that every organisation capable of online invoicing can send an online invoice to the consumer, without the consumer having previously entered into an individual agreement with the invoicer regarding the invoice.
Using the feature requires that the consumer has activated the desired service(s) either on a mobile device or in their online bank. In addition to commissioning, the consumer must provide the necessary invoicing information to the invoicer in order to direct the invoice to the correct invoicing channel.
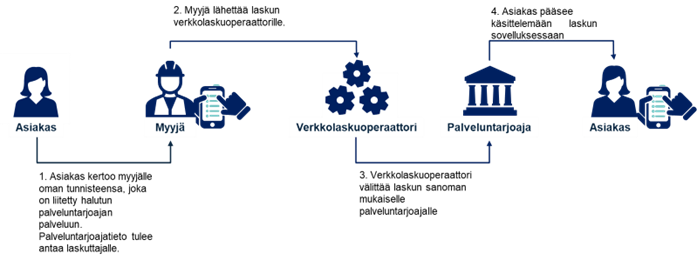
Invoicing solutions
In order for an invoicer to start one-time consumer invoicing, the invoicer must have
- invoicing software capable of e-invoicing,
- an e-invoice operator compatible with the desired service(s) and
- valid agreements with service providers.
1. Mobile payment solutions
Consumer invoicing can also be done with mobile payment tools. Mobile payment services include e.g. MobilePay and Siirto
1.1 MobilePay invoicing solution
- MobilePay invoicing requires a capable invoicing system and an e-invoicing operator. In the invoicing system, an invoice in the Finvoice format is sent to the operator according to the operator’s instructions.
- The invoice is routed to the operator’s API based on the mobile phone number that serves as the online invoicing address and the operator ID, from which the operator forwards the payment information to MobilePay.
- The payment information has the basic invoice information, and it can also include a link to an invoice image in the operator’s invoicing service, with which the more detailed content of the invoice can be viewed.
- In order to use MobilePay, the invoicer must identify themselves as a MobilePay invoicer and authorise the e-invoice operator in the service to allow the relaying of invoices.
- MobilePay also has the option of making payment requests using the service portal.
1.2 Siirto invoicing
- Commissioning Siirto invoicing requires an invoicing system suitable for e-invoicing and a Siirto-compatible e-invoicing operator. The invoicer must also be a customer of Nordea Bank plc. Consumers can receive Siirto invoices using Nordea’s Siirto or OP’s Mobiili or Pivo applications.
- When commissioning, the invoicer concludes an agreement on Siirto services with Nordea. After concluding the agreement, the invoicer must send the Siirto key to their Siirto-compatible e-invoicing operator.
- The routing information of a Siirto invoice consists of the recipient’s mobile phone number or Finnish business ID, which means that invoices can also be sent to companies.
2. Mailbox services
Various e-mail applications are an alternative to online banks or mobile payment applications. These serve as services for receiving invoices and also paper letters for consumers. Mailbox services also require an invoicing system that supports processing e-invoices, so that the invoices can be pre-filled for the consumer to pay.
From the point of view of the sending company, online mailbox services are also a broader communication solution with various opportunities for value-added services.
2.1 Kivra
- The digital mail service Kivra offers consumers a free option for receiving online mail. The service also receives invoices, which can be paid directly in the service.
- To start using Kivra, the sender must contact their e-invoice operator and find out the possibility of using Kivra’s service channel, or build a direct integration. Once the service bus has been confirmed, the service can be activated by agreeing on use with Kivra.
- It is also possible to use Kivra for relaying other mail, such as pay slips, tickets etc.
2.2 OmaPosti
- OmaPosti is Posti Group’s solution for relaying digital documents. The service allows for relaying letters and invoices. Any address-bearing communication can be delivered to OmaPosti.
- Consumers can pay their invoices in the OmaPosti service using a payment card, by bank transfer from their payment account or with the Pivo application.
Targeting is done using a combination of the recipient’s name and address or with a personal identity number. - To use OmaPosti, contact the e-invoice operator or printing service and find out the possibilities of using the service.
More on Posti’s website at www.posti.fi/omaposti or www.ipost.fi
3. Solutions based on e-invoices
In order to send recurring e-invoices, an invoicer notice (SI message) is required, with which the invoicer adds themselves to different banks’ lists of e-invoicers. The invoicer notice is generated in message form using, for example, the program on the finvoice.info page, and the generated invoicer notice is sent to the invoicer’s bank. The message addresses the form of and need for invoicing.
A one-off e-invoice can also be delivered to some banks directly using the consumer’s e-invoice address. The e-invoice address is in the IBAN format. It should be checked whether the invoicing system can prepare the invoice as an invoice for a private individual with an e-invoice address.
The first invoice of recurring invoicing
An invoicer who has already sent SI messages to the banks can directly start invoicing as one-time invoicing. This makes it possible for the invoicer to send the first invoice to the customer in the online bank, and after paying this invoice, the customer can activate recurring invoicing. Once recurring invoicing has been activated, the invoices will receive an RI message, which replaces the consumer’s e-invoicing address in the invoicer’s customer register used for one-off invoicing.
Summary
Several services already exist to address one-off consumer invoicing. The availability of the services depends on the service channels of the invoicer’s e-invoice operator.
When implementing new services for consumer invoicing, it is worth contacting the e-invoice operator to ask for views and instructions for implementing the services. E-invoice operators can assist with the commissioning.
